After recently looking at E-band for 5G fronthaul and midhaul, in this post, we’re going to focus on other compelling E-band mmW use cases.
As mentioned in that previous post, the demand for E-band is expanding rapidly due to the growing need for ultra-high capacity and the move to disaggregated network architectures.
Now, let’s examine four additional use cases that are well served by the E-band millimeter wave (mmW) frequency range.
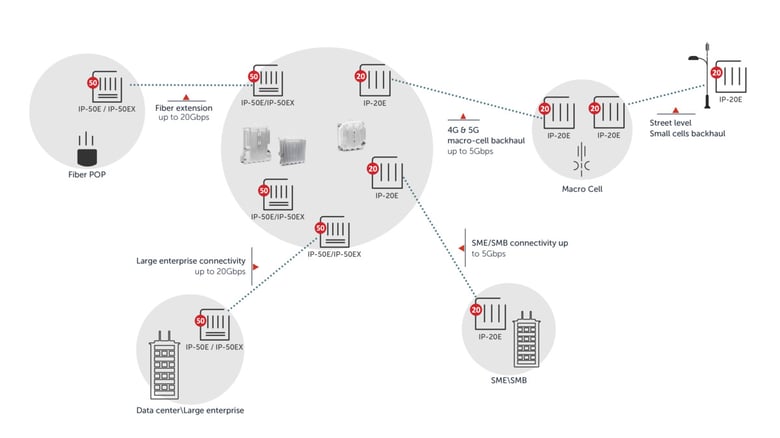
Fiber extension
To meet growing coverage and capacity requirements, the successful deployment of 5G often necessitates the smart combination of fiber and wireless technologies, especially as the reach of fiber is often limited by cost or infrastructure considerations.
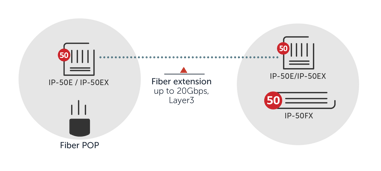
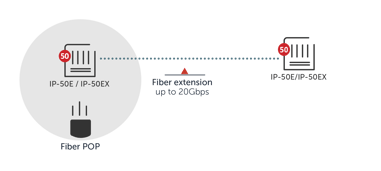
In this fiber extension use case, a mobile network operator (MNO) uses E-band mmW for fiber point of presence (POP) connectivity.
In cases of “last mile” connectivity over a typical 1-2 kilometers, E-band mmW is a good choice as it can deliver the 10-20 Gbps usually required for such a use case and can do so with high reliability. E-band mmW can be combined with traditional microwave in a multiband configuration when longer links are required.
Large enterprise connectivity
In this large enterprise connectivity use case, an internet service provider (ISP) offers a high-capacity fixed wireless service that connects a large corporation. Such connectivity often includes links between multiple large company buildings within a spread-out organizational campus or across busy city streets.
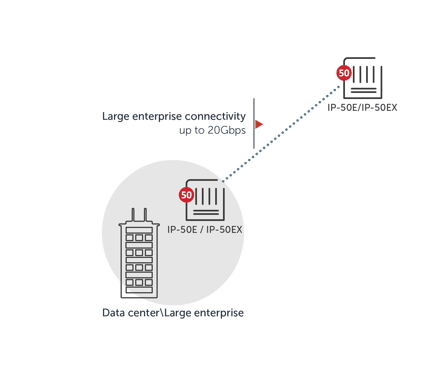
In such cases, E-band mmW can deliver 99.999% (five-nine) availability over links of up to 1-2 km, or four-nine availability for links up to 2-3 km.
Large enterprise connectivity usually requires somewhere around 4-10 Gbps, while intra-campus connectivity calls for 2-5 Gbps. In these cases, 10 Gbps is usually more than sufficient.
SME/SMB connectivity
There are also similar use cases involving ISPs connecting smaller enterprises/businesses (SMEs/SMBs) and smaller campuses.
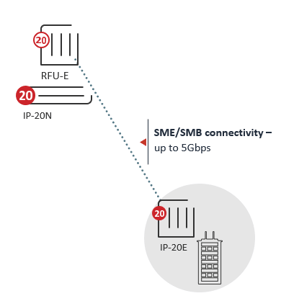
In terms of reach, like with the previous large enterprise use case, E-band mmW supports five-nine availability over links of 1-2 km. These use cases typically require up to 2.5 or 5.0 Gbps.
5G/4G macrocell and small cell backhaul
In the 5G/4G macrocell and small cell backhaul use case, an MNO uses E-band mmW to connect street-level small cells to a macrocell, which in turn connects to the aggregation site towards the core network.
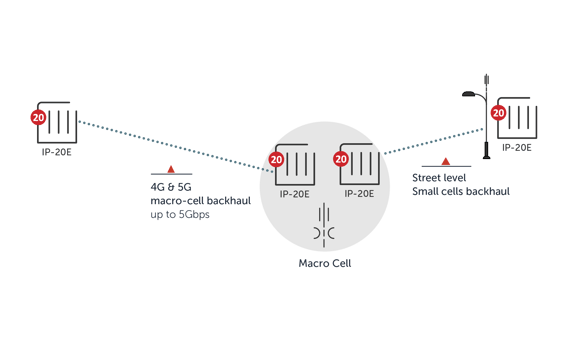
At the street level, there is a need for a simple and cost-effective all-outdoor solution with an integrated antenna, with an appearance similar to that of a Wi-Fi hotspot. Deployed in a “mesh-like” configuration, small cell links range from a few hundred meters up to 1 km.
Typically a capacity of 2.5 Gbps is sufficient for small cell backhaul, with up to 5 Gbps needed for aggregation points.
E-band mmW advantages
To understand the advantages of 5G millimeter wave E-band for the above use cases, it’s useful to quickly compare E-band to its two main technological alternatives, fiber-optic cable and traditional microwave. (see also: millimeter wave 5G)
Fiber is often limited when it comes to “last mile” access connectivity. Indeed, in many cases, FTTx does not actually reach the desired end point (e.g. premises, buildings or homes) due to cost and implementation obstacles. Right-of-way issues related to digging trenches and laying fiber often make this option simply impossible to implement.
Traditional microwave suffers from limited and congested spectrum, especially in urban areas, and typical licensed spectrum channels are very narrow when compared to E-Band mmW. Due to limited available spectrum in these bands, lower channel bandwidth and wider antenna sizes, deployment of traditional microwave in dense urban or metropolitan areas is problematic.
Expand Your Fiber Reach - Watch Our Video
For the use cases described above, E-band mmW offers many advantages:
- high spectrum availability and ultra-high bandwidth (up to 20 Gbps) vs. traditional microwave
- wide range of channel BW sizes, with channel separation ranging from 62.5 MHz to 2 GHz
- very low latency performances (even lower than 20 microseconds) due to wide channels
- 999% (five-nine) availability at ranges of up to 1-2 km
- small form factor and physical footprint
- low spectrum fees vs. traditional microwave
- minimization of interference due to utilization of very narrow antenna beams
- reliable performance guaranteed under different weather conditions
- rapid installation and return on investment (ROI) vs. buried fiber
- low fixed costs and low total cost of ownership (TCO) vs. buried fiber
To learn more about E-band mmW solutions


